What are the different types of computer networks based on their size?
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a network that connects computers and devices within a small geographic area, such as a building or campus.

Advantages:
- High data transfer rates
- Easy to set up and maintain
- Cost-effective
- Secure, as the network is isolated from the outside world
Disadvantages:
- Limited geographic range
- Expensive to expand beyond the initial setup
- Limited scalability
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN is a network that connects multiple LANs and other networks over a large geographic area, such as a city, country, or even the whole world.

Advantages:
- Large geographic range
- Enables communication over long distances
- Supports a variety of communication technologies
- Scalable and flexible
Disadvantages:
- Expensive to set up and maintain
- Lower data transfer rates compared to LAN
- Requires specialized hardware and software
- Security concerns due to wide accessibility
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A MAN is a network that covers a larger geographic area than a LAN, but smaller than a WAN. It is typically used to connect multiple LANs within a city or metropolitan area.
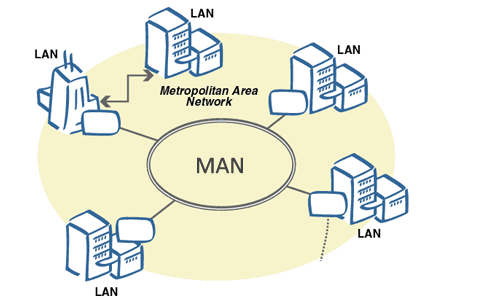
Advantages:
- Larger geographic range than LANs
- Faster data transfer rates than WANs
- Enables communication over a larger area
- Cost-effective compared to WANs
Disadvantages:
- Limited scalability
- Requires specialized hardware and software
- Security concerns due to wide accessibility