Types of Network Topology
Computer networks are a crucial part of modern businesses and organizations. They enable communication, collaboration, and information sharing among employees and clients. There are various types of network topologies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we'll explore the three main types of network topologies and their strengths and weaknesses.
- Bus Topology
The bus topology is the simplest and most common type of network topology. It consists of a single cable that connects all devices in the network. Each device is connected to the cable via a T-connector or tap. Bus topology is ideal for small networks with a few devices, such as in a small office or home. However, it has some drawbacks that limit its scalability and reliability.
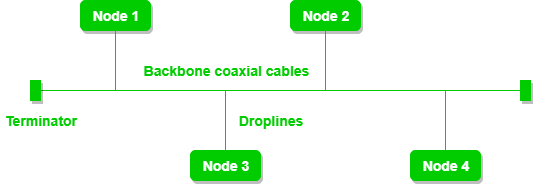
Advantages:
- Easy to set up and maintain
- Cost-effective for small networks
- Requires less cabling than other topologies
Disadvantages:
- Single point of failure - if the cable is cut or damaged, the entire network goes down
- Performance can degrade as more devices are added to the network
- Difficult to isolate problems in the network
- Star Topology
The star topology is a more sophisticated network topology that features a central hub or switch that connects all devices in the network. Each device is connected to the hub via a separate cable. This topology is commonly used in larger networks that require more scalability and fault tolerance.

Advantages:
- Easy to add or remove devices from the network
- Fault tolerance - only the affected device is affected in case of a failure
- Easy to identify and isolate problems in the network
Disadvantages:
- Requires more cabling than other topologies
- Dependent on the central hub or switch - if it fails, the entire network goes down
- Costlier to implement than bus topology
- Ring Topology
The ring topology is a circular network topology where each device is connected to two adjacent devices, forming a closed loop. Data is transmitted around the loop in one direction, and each device receives and passes on the data to the next device in the ring. This topology is less common than the bus and star topologies, but it has some unique advantages.
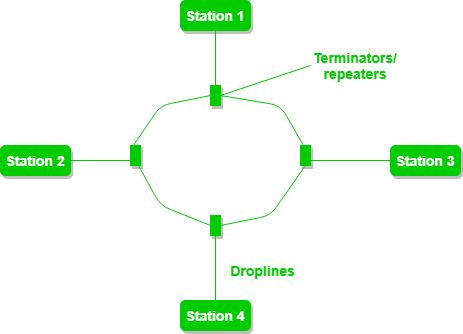
Advantages:
- Equal access to network resources for all devices
- No central point of failure
- Data transmission is efficient and fast
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to add or remove devices from the network
- Failure of a single device can disrupt the entire network
- Performance can degrade as more devices are added to the network
- Tree Topology The tree topology, also known as hierarchical topology, is a type of network topology that combines the features of the bus and star topologies. It is a hierarchy of bus topologies that are interconnected through a central root node. This topology is commonly used in larger networks that require more scalability and flexibility.
 Advantages:
Advantages:
- Provides a logical and organized structure to the network
- Easy to add or remove devices from the network
- Allows for better management and control of network traffic
Disadvantages:
- Dependent on the central root node - if it fails, the entire network below it is affected
- More complex and difficult to set up and maintain than other topologies
- Requires more cabling than other topologies
- Hybrid Topology
The hybrid topology is a combination of two or more types of network topologies, such as star-bus, star-ring, or mesh-bus. This topology is commonly used in large and complex networks that require high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability.

Advantages:
- Offers high availability and fault tolerance
- Provides multiple paths for data transmission, which increases network reliability and performance
- Can be customized to meet specific network requirements
Disadvantages:
- Complex and difficult to set up and maintain
- Requires a significant amount of cabling and hardware
- Costlier to implement than other topologies